Basic C# OOP Concept
There are many explanations that we can find in internet about C# OOP, but here in my article I will give a very simple example. In this article, I will use a “House (like the houses we live in) “as a real-time example for easy understanding of OOP Concept in C#.
1. Class
Class is a like a Blueprint.
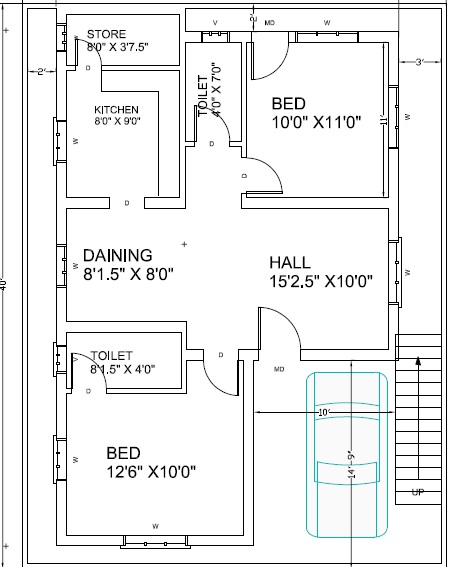
Blueprint is outline drawing of our actual plan. For example if we plan to build our new house, the Engineer will explain our new house plan with a blue print as shown in the image below. Once we finalized the plan the engineer will start building the house with same plan.
Same like blueprint class is an outline of program. Using the class we can write our own method and declare the variables and using the objects we can access the class Method and Variables. The class will be complete with Variables, Methods and Objects.
For more easy understanding of OOP with real world example here I have explained a class with House.
We can imagine a House as an example for a Class. In a house, we will have rooms like living room, bedroom, kitchen and items like TV, fridge etc. House owner can access and use all the rooms and rooms’ items. Same like this in a Class will have a group of Methods and Variables.
Rooms and Rooms’items are example for Methods and Variables. So now, we have a complete house with all rooms and rooms’items. House owner can access and use all the rooms and Rooms’ Items. To access and use a Class, methods and variables here we use Objects. Objects are instance of a class. We will see details about objects in the next section.
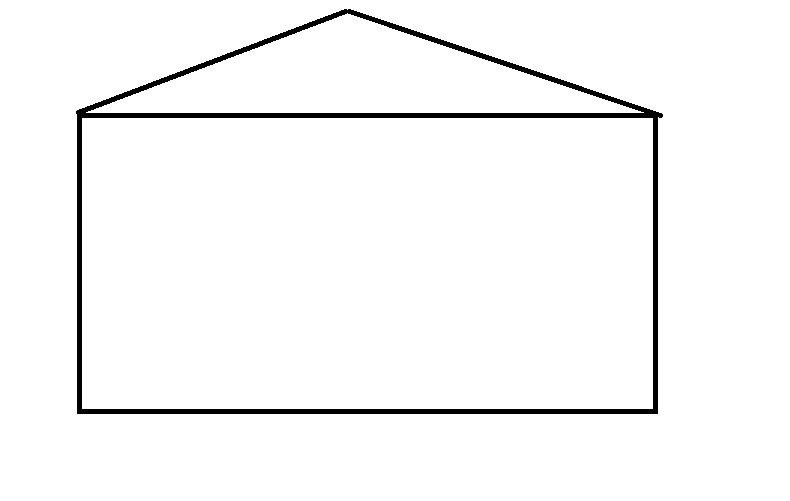
What will happen if there are no rooms and items in a House? It will be empty and no one can use the house until it has all the rooms and Items. See the below image as an example for the empty house.
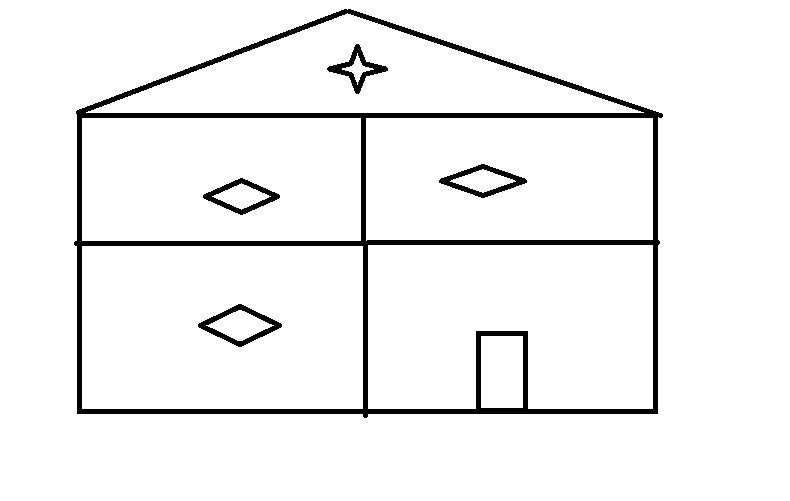
Now this empty house is a Class. So what is the use of a Class without Methods and variable. Now let’s see an example for a Complete House with Rooms and items.
So here, we have a complete house. Similarly, the Class will be complete with group of Variables, Methods and Objects. We can see details of all this in next sections of this article.
Class and objects are the base concept of OOP – Object Oriented Programming.
Class should be started with the Keyword class and next we give the name for our class we can give any meaning full name as Class Name, next we will have the Open and close brackets.
| |
2. Object
As we have already seen that, House Owner will access and use all the Rooms of the House and its Items. Similarly, to access all Class Method and Variable we use Objects. We can create one or many object for a same Class. Example we can say for a house there might be one or many owners.
objHouseOwner is the Object for a class which will be used to access all variable and Method of a class.
| |
3. Variable
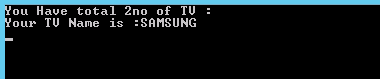
Variables are used to store our value. Our value can be numeric or characters for example to store a Phone no we can use int type variable and to store our name we can use string type variable with name for each variable.
Variables can be local or Global. For Example, we can say if we buy a new TV , TV Service man will come and setup the TV in our home. He will give his contact number for future contacts. Usually what we do is take a memo paper and write his contact number and keep it in a common place or in a wallet of ours.
If we keep the memo in a Common place everyone who is visiting our house can see that contact number. Global or public variables are similar to this. If we declared the variable as Global, All the Methods inside the class can access the variable. If we store the memo Only in our wallet, we can see the contact number. Local or private variables are similar to this.
Syntax for variable:
Access-Modifiers Data-Type Variable-Name
By default the Access-Modifiers are by private, we can also use public to variable.
Example of Variable:
| |
In Above example program I have declared two variables inside a class. In main method I have created object for class. Here we can see using the object we can access the variable of a class and display the output.
Main Method is the default Method of C#, where every console and windows application will start the program execution, In the Main Method, we can declare the Object for the class and use the object, and we can access all variables and Methods of a Class. For example, we can say there will be entrance gate for every house. Using the entrance gate we can enter inside our house. Similarly, to run our program there should be some default program execution starting Method. Main method will be useful in this program execution starting point. Whenever we run our C# Console or windows application, first the Main method will be executed .From the main method we can create an object for our other classes and call their Methods.
4. Method or Functions
Method is a group of code statement .Now here we can see the above example program with method.
| |
Most of developers were wondering about what is the difference between the Method and Function, both Methods and Functions are the same. Here in my article, I will use Method instead of functions. However, there is one difference in Methods and Functions, In OOP Languages like
C#, Javaetc. We use the term Method while the non-OOP programming likeCetc. we use the term Function.
What is the use of Methods? Another real-time example let’s take our mobile phone, we can say as we have Mobile phone and store many Songs in it. However, we always like to listen to the selected songs. It will be boring and hard for us to select our favorite song every time and play it.
Instead of doing the same work repeatedly, we use the playlist. In playlist, we can add all-favorite songs of ours. Just click on the playlist of our collections and listen to the music. This will make our work easier and we don’t need to do the same thing again and again. Methods are used like a playlist where we can write all our repeated code in one Method and just call the method wherever we needed.
In a house, there might be one big room or multiple rooms but each room will have different facilities, similarly in a class we can write one or multiple Methods. In a house, there might be two or three Bedrooms. Here the room name is Bedroom, but each bedroom can be different by size, color etc. This means same Rooms with different type. Similarly, in a class we can create more than one method with the same name but different parameter. In OOP it’s called as Polymorphism we can see details about Polymorphism later on in this article.
Syntax for the Functions
Access-Modifiers Return-Type Method-Name (Parameter-List)
- Access-Modifiers: We will see more details about this Topic later on.
- Return-Type: If our Method returns any value then we use the return Type with any Data Type as String, int etc., if our Method does not return any value then we use the type “Void”.
- Method-Name: Here we give our Name for every Method, which we create
- Parameter-List: Parameter-List or Arguments, which we pass to the function.
Here is an example of Method:
- Method with Void Type:
Void is a keyword which will not return any data from the Method, for example we can see the below Method with void Type, here in this method we display all our output using the
Console.WriteLineand have used theConsole.ReadLine());to get the Input. This Method has all Input and Output Operation but this method don’t return any value.
| |
- Method with Return Type:
Method with return type will return some result, which can be used in our program, for example, here we have Method TVNAME with return Type as
String. We can say in our home we might have a TV in our LivingROOM and in the parent’s bedroom and also in kids bedroom .We might have different TV brand in each room, suppose if we want to know each room TV Brand Name then we need to enter the same code 3 times. Instead of writing the same code again, we can use a method with Return Type.
| |
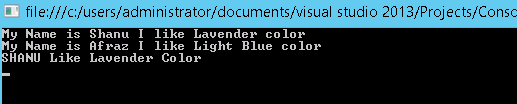
- Method with Parameter-List: So far, we have seen methods without arguments. Arguments are used to pass some data to the Method to do our process in a better way. For example, we can say we want to do a painting, to our bedrooms. We need to get the opinions of all the member of the house in order to know there choices of color for each bedroom, we can pass the member Name and their favorite color as parameter to a Method.
| |
Same Method name with different arguments are called as Method over loading, here we can see below .Both Method has the same name but it has different arguments.
| |
The Complete Class with Main Method Example:
| |
The Output of above class is here:
5. Access Modifiers
Access Modifiers are nothing but the Usage and Limitation of our type like variable, Methods and Class. For Example we can say it as a security limit. This six are the basic Access modifiers which we used in our C# Class/method and in Variables.
Private
Let’s take our House Example .We will have a Security Guard in House, His duty is till the Entrance of the house. He cannot go inside the house and access all the things. In this case we can create a SecurityGuardClass and declare the variable and method for Security as private .
Public
House Owners are public to the class where they can access all classes related to the House. They have no restrictions to access their house.
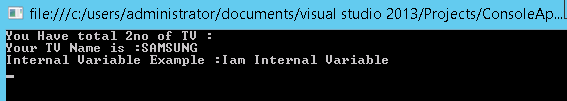
Internal
Access limit of variable or method is within a project. For example let’s consider in our project we have more than one class and we have declared a variable as internal in one class. Let’s see an example program for internal variable.
| |
Protected
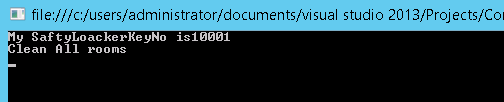
Only the main class and derived class can have access of protected variable or method. For example servants and Guests are example for the Protected. For Example Servants can go to all room and do cleaning and other activates. However, they have limitations of access in the house, as they cannot take rest in a bed of house owner.
Protected Internal
Protected Internal variable or Method has limitation with in a project of class or Derived class. Here is a sample program for Protect Internal Variable .In this example I have used the Inheritance .we will see in detail about Inheritance more detail in this article.
| |
The main and major things we need to know in OOP concept are Encapsulation, Abstraction,Polymorphism and Inheritance. We will discuss them in detail in this article.
6. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is to hide the member or variable to outside class. In our house example, I have already told that House security guard limitation is till the entrance of the house. The security guard doesn’t need to know about what is happening inside the house. Therefore, the House Owner will hide all the happenings to Security guard for more safety. The hiding and limitation are called as Encapsulation.
For example, we have two Classes the first one is Houseclass and the other class as houseSecurityClass.
Here we can see all the variables are wrap into a class where houseSecurityClass is set as public, so the Houseclass can access that, but houseClass has both Public and private variable where the private variable of a class cannot be accessed outside of the class.
| |
7. Abstraction
Abstraction is to show and share some common information to the user. Let’s take our House example, in our house we will have servant, servants can go to all rooms and do cleaning and other works. The house owner can give full rights or some partial rights to the servant for accessing his house. Here we can see an example program as private declared variables and Methods are not shared with servant but the public variable and Methods are shared with servant.
| |
8. Inheritance
Inheritance is used to reuse the code. In Protected Internal Access modifier section we have already seen an example program for Inheritance. Inheritance is nothing but accessing and using all base class variable and methods in the Derived Class. Inheritance can be
- Single level Inheritance
With one Base class and one derived Class for example.
| |
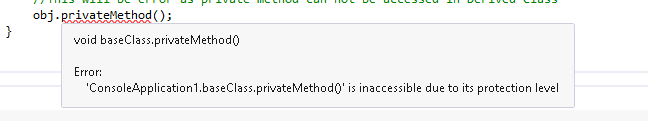
The Error is:
Some time users might be not clear of what Base class is and what Derived class is. Base class is the super class and derived class is the classes which inherit the base class.
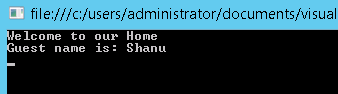
Here we can see a simple Inheritance where the base class is the GuestVist and derived class is the HouseOwnerClass. Here HouseOwnerClass class inherits the base class of GuestVist
- Multi level Inheritance
With more than one Derived Class for example. Here we can see an example first base class is derived in DerivedClass1 and then the DerivedClass1 is derived in DerivedClass2 .Now from DerivedClass2 we can access both baseClass and DerivedClass1 variable and methods.
| |
Multiple Inheritance
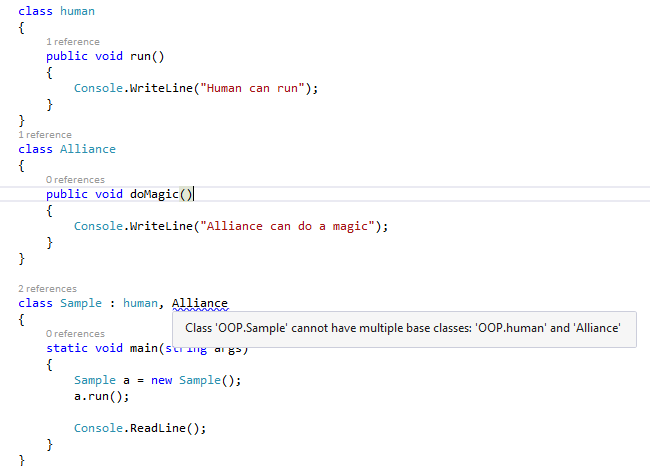
- Will the .Net Support Multiple Inheritance? The Answer to this Question is No. In C #, it’s not possible to write a Multiple Inheritance using Class. What is Multiple Inheritance? Multiple Inheritance is nothing but we can have more than one class and we can inherit both Classes in our derived class.
- What will happen if I write a Multiple Class Inheritance Using C#?
Let’s take our example House .Here we have the derived Class as
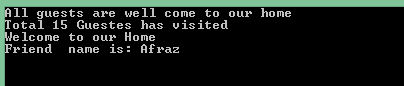
HouseOwnerClassand have Two More classes asGuestVistandFriendsandRelationsClass. Now suppose for our house both Guest and Friend have visited. For this, we write above three classes and inherit the two classes in our derived class. When I write the Multiple Inheritance in C #, it will display the warning message during our code and execute our program. See the below image which shows the Warning error message while I write Multiple Inheritance.
* Then how can we use the Multiple Inheritance
Interface will be used for Multiple Inheritance.
9. Polymorphism
Ploy means more than one form. In the beginning of the Article at Method Section, we have already seen an example of Polymorphism. Same method name with different parameter is an example for the polymorphism. Method Overloading and Method Overriding will be used in polymorphism. Polymorphism have two types of execution one is Compile Time Polymorphism and the other one is called the Run time Polymorphism.
- Method Overloading
Method overloading are nothing but same Method name will be used for more than one method with different Argument.
Here is an example program for the Method Overloading. As we can see here Method name BedRoom has been used for two Method but the parameter for both methods are different.
| |
- Method Overriding
The difference between the Method Overloading and Overriding are.In Method Overloading we will have same method name with different argument. In Method Overriding we will have same Method Name same Argument and same type but method overriding can only be used in the derived class, Method Overriding cannot be done in the same class. We will see how Method Overriding can be used in Abstract Method, Virtual Method and in Sealed Method kindly refer to that section in this article.
10. Abstract Class/Method
- Abstract Class: Abstract class will have a keyword
abstract.
The Abstract class will be as a super class for all our class. Abstract class cannot be accessed by an object, which means we cannot create an object for an abstract class.
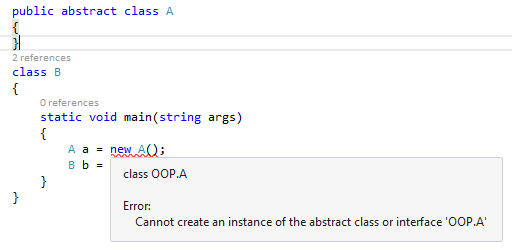
- What will happen when we create an object for an Abstract Class?
Here we can see an error warning message as “An instance of an abstract class cannot be created” when I try to create an object for my abstract class.
Abstract class can have both Abstract Method and normal Method. In Abstract Class at least one Abstract Method should be declared. In addition, derived class should override the abstract method. To access the abstract method we should use the “override” keyword in our derived class.
- What will happen if we create an abstract method but which is not override in derived class?
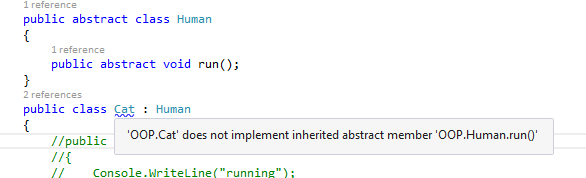
Here we can see an abstract class has an abstract method, But the abstract method is not override in the derived class. See the below image for the warning message displaying as class must implement the abstract member.
Here we can see an example of Abstract Class and for Abstract Method in detail. In this example, we can see an abstract class, which has normal Method and Abstract Method. Abstract Methods; do not have body part in Abstract Class, which means we can only declare an Abstract Method at Abstract Class, There should be minimum one Abstract Method in an Abstract Class.
| |
11. Virtual Class/Method
Virtual method is very useful in our day-to-day programming.
- What is virtual Method and what is the use of Virtual Method?
Take our House example one guest confirms, as today total five persons will visit your home. For this, we write a function as message display as five Guest visiting our home. Once Guest visits, we see their total 20 persons have visited. In Some cases it might be increase or decrease we will come to know when they reach us.
In that case, the guest will be as a Separate Class and House will be as separate class. Without changing the message in Guest class how can we change the data in our Derived class?
- What is the Difference between Abstract Method and Virtual Method?
Both similarities use the override keyword. Abstract Method can only be declared in Abstract Class, which means no body part for abstract method in Abstract class. However, for virtual it can have body part.
See the example program below. Here we have both Abstract Method and Virtual Method.
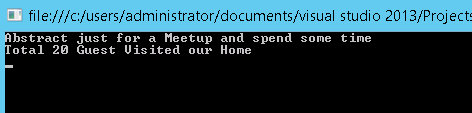
In Abstract class, the virtual method says as total five guests but in the derived Class program, the message was override as 20 guests. See the final output in below. Guess what will be displayed for Virtual Method? Will the result be 5 Guests or 20 Guests check for the output below the program.
| |
12. Sealed Class/Method
Sealed Class:
As name says this class cannot be inherited by other classes.
Take our House Example. In a house, the Houseowner can have a secret room, as might be official or financial rooms. The owner don’t want others to access his official room. The sealed class will be useful in those cases. Sealed class can be declared using the keyword Sealed. If one class is declared as Sealed, it cannot be inherited in other derived classes.
- What will happen when we inherit sealed class in our derived class?
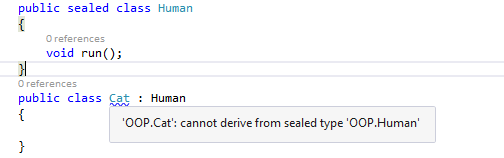
Let’s see an example when I try to inherit my sealed class from my derived class. It shows me the below warning message.
Here we can see an example program of Sealed Class.
| |
Sealed Method:
If we declared a method as sealed that specific method cannot be override in the derived class.
Let’s see our house class here I have base class with Virtual Method and virtual Sealed method.
The Virtual method can be override in the derived class .But the Virtual Sealed Method cannot be override in sealed class.
13. Static Class/Method
We have already learned about what is Sealed Class in this Article; now let’s see what are Static Class and Static Method. Both Static and Sealed Class cannot be inherited.
- What is the Difference between Static Class and Sealed Class?
We can create an Object (instance) for the Sealed Class, we can see in my sealed class section I have created a sample Sealed class and in Main Method I have created an object to access the sealed Class. And in a Sealed Class both Static and non-Static methods can be written.
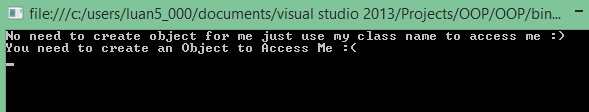
But for a Static Class it’s not possible to create an Object. In Static Class only Static members are allowed which means in a static Class it’s not possible to write non-static method.
We can say our main method as an example for the Static method. When we create a console application in c# we can see each class will have a default main method. In my article I have explained that when an Console or Windows application start execute first the main method will be executed .There is no need to create an object for the main method since it was been declared as a static method.
static void Main(string[] args)
Another interesting one in Static class is that memory will be allocated for all static variable and methods during execution but for the non static variable and methods memory will be allocated only when the object for the class are created. Let’s take our same sealed class Example for our static Class and method.
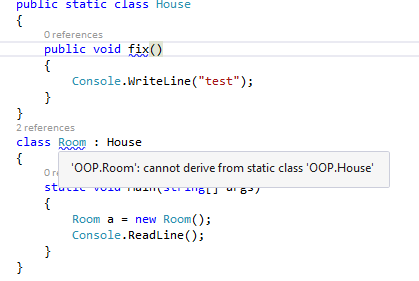
- What will happen when we inherit Static class in our derived class?
Let’s see an example when I try to inherit my static class from my derived class. It shows me the below warning message.
- What will happen when we declare non-Static method in a Static class?
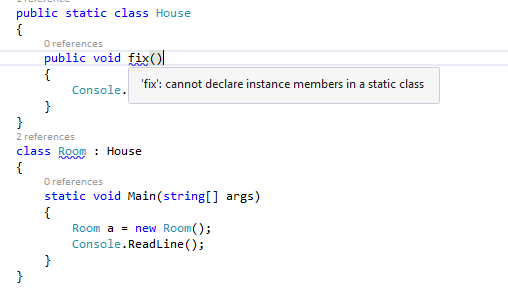
Let’s see an example when I try to create a non-Static method at my Static Class.
- What will happen when we create an object for the Static class?
Let’s see an example when I try to create an object for my Static Class.
When we run the program we get the error message as Can not create an instance of a static class
- How to call the Static Class Method and variable without creating the Object?
It’s simple just we can use the ClassName.Variable or Method Name for example OwnerofficialRoom.AllMyPersonalItems();
See the below example with Static class
| |
- Is that possible to create a Static Method in non-Static Class?
The answer is yes. We can create a Static Method to the non Static class. No need to create an object to access the static method in non-static class. We can directly use the class name to access the Static method. See the below example with Static method in non-static Class.
| |
14. Interface
Interface is same like abstract class but in Interface we will have only method declaration but in abstract class we can have both method declaration and method definition .Methods of Interface must be implemented in a implementing class.
See the below Example program for an Interface. All the methods of Interface have been implemented in the class. As I have already told you that c# don’t support multiple inheritance for using multiple inheritance we can use Interface.
This below program is an example for multiple inheritance using Interface.
| |
In some cases we need to have certain methods which will be used in many derived classes. Each derived can implement different functionality for those Methods. In These cases, we can use the Interface.
We can say our Guest and house example. For Guest the Welcome Message and No of Guest Function are common, but it will be different for different owners in the same house, Guest might a fathers guest, Mothers Guest, Children’s Guest or Family Guest. Each guest can have different welcome message subject, but the functions are same as Message .let’s consider now Father is a Class, Mother is a class and Children are one Class. Both guestWelcome Message and Noofguest method are same for all. In this case, we can create an Interface and declare both methods in the Interface. All father, mother and Children Classes can inherit the interface and write their own method details.
Interface is similar to Abstract class but the major difference between the Abstract Class and the Interface are .In Abstract Class there can be both Abstract Method and Non Abstract methods .But in Interface all methods are abstract by default which means there is no non Abstract type method in the Interface. All the Methods declared in Interface should be override in the derived class.
What will happen when non-abstract methods with body part are declared in an Interface?
It will display the warning message as unexpected modifier in Access modifier part and Unexpected Method body error warning at message Body.
This article repost from here under markdown format. Thank you!